
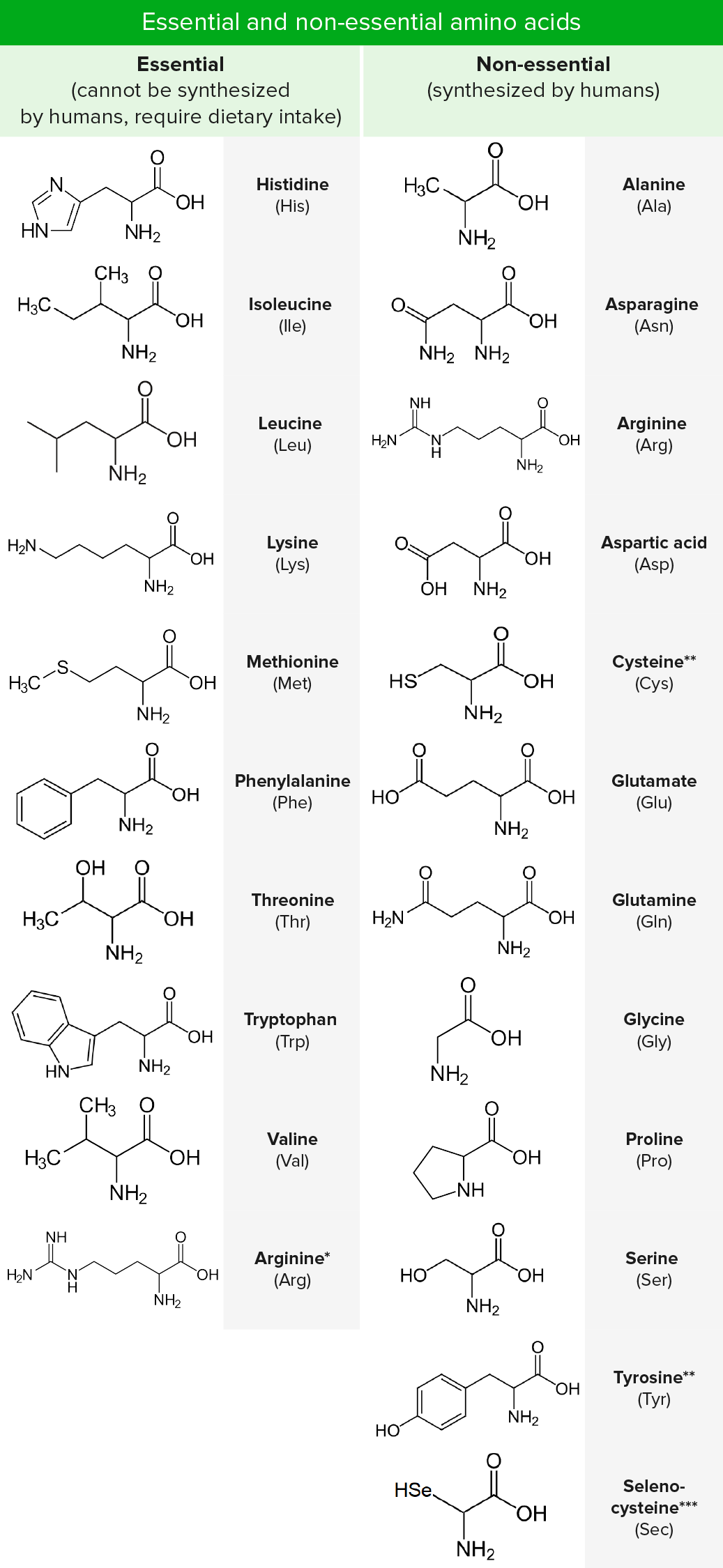
Proteins were found to yield amino acids after enzymatic digestion or acid hydrolysis. The first use of the term "amino acid" in the English language dates from 1898, while the German term, Aminosäure, was used earlier. The unity of the chemical category was recognized by Wurtz in 1865, but he gave no particular name to it. The last of the 20 common amino acids to be discovered was threonine in 1935 by William Cumming Rose, who also determined the essential amino acids and established the minimum daily requirements of all amino acids for optimal growth. Glycine and leucine were discovered in 1820. Cystine was discovered in 1810, although its monomer, cysteine, remained undiscovered until 1884. In 1806, French chemists Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin and Pierre Jean Robiquet isolated a compound from asparagus that was subsequently named asparagine, the first amino acid to be discovered. The first few amino acids were discovered in the early 1800s. 4.2 Standard vs nonstandard amino acids.4 Occurrence and functions in biochemistry.3.1 Table of standard amino acid abbreviations and properties.3 Physicochemical properties of amino acids.This convention is useful to avoid various nomenclatural problems but should not be taken to imply that these structures represent an appreciable fraction of the amino-acid molecules. The systematic names and formulas given refer to hypothetical forms in which amino groups are unprotonated and carboxyl groups are undissociated. The Commission justified this approach as follows:

For example, the systematic name of alanine is 2-aminopropanoic acid, based on the formula CH 3−CH(NH 2)−COOH. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.Īmino acids are formally named by the IUPAC-IUBMB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature in terms of the fictitious "neutral" structure shown in the illustration. In the form of proteins, amino acid residues form the second-largest component ( water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Īmino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most prevalent are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Structure of a generic L-alpha-amino acid in the "neutral" form needed for defining a systematic name, without implying that this form actually exists in detectable amounts either in aqueous solution or in the solid state.Īmino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
